Trinidad and Tobago is a country located in the Caribbean Sea. It is the southernmost island in the Caribbean and is known for its stunning beaches, lush rainforests, and vibrant culture. The official language of Trinidad and Tobago is English, although many locals also speak Spanish, French, and Hindi. According to homosociety, the population of Trinidad and Tobago is estimated to be around 1.4 million people. The currency of Trinidad and Tobago is the Trinidad & Tobago Dollar (TTD). Religion plays an important role in the life of many citizens with Christianity being the dominant religion followed by Hinduism, Islam, and other faiths. The economy of this country relies heavily on oil production as well as tourism which brings in millions of visitors each year to enjoy its tropical climate and vibrant culture.
Prehistory
The Little Antilles were populated from the Orinoco region about 5000 – about 4000 BC. From about 1000 BC created sweat farming (for the cultivation of mainly maniacs), along with hunting and fishing, the foundations for resident villages. Ceramics were introduced at about the time of the birth of Christ, most likely by the Aryan-speaking people; the islands were also populated by Caribbean tribes. Compare Central America (Prehistory).
History
Both Trinidad and Tobago were visited by Columbus in 1498. In 1616, the British tried to settle in Tobago but were driven by the Caribbean. The Spaniards ruled Trinidad until 1797, when the island was conquered by the British. It came to Britain through the peace of Amiens in 1802. After a long period of French influence, Tobago also came under British rule in the late 18th century. A tropical plantation economy – tobacco, cocoa, sugar – was developed in Trinidad and Tobago during the 18th and 19th centuries. Since the Native American population gradually died out, production was based first on African slaves and then on Asian labor (mainly Indian). In 1889, Trinidad and Tobago were united and gained the position of British Crown Colony. See abbreviationfinder for geography, history, society, politics, and economy of Trinidad and Tobago.
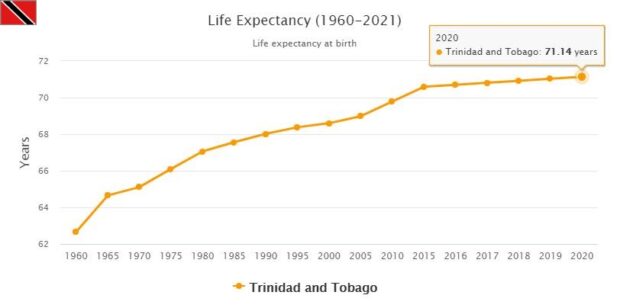
- COUNTRYAAH.COM: Provides latest population data about Trinidad and Tobago. Lists by Year from 1950 to 2020. Also includes major cities by population.
Oil became an increasingly important export product during the 20th century and has completely dominated Trinidad and Tobago’s economy for the last few decades. In the 1920s, political development towards self-government began, and in 1962 Trinidad and Tobago gained independence within the Commonwealth. Eric Williams, leader of the People’s National Movement (PNM), dominated Trinidad and Tobago’s political scene as prime minister in 1962–81. In 1976, Trinidad and Tobago were transformed into a republic within the Commonwealth with Ellis Clarke as the first president. In connection with an increasingly difficult economic situation, PNM was defeated in 1986 by a new party, the National Alliance for Reconstruction (NAR), led by ANR Robinson, who was appointed prime minister in 1987. NAR, through agreement with the International Monetary Fund, enforced a tough economic policy, which aroused strong opposition. In July 1990, in a bloody coup, a militant Muslim sect, Jamaat al-Muslim, took control of the House of Parliament and kidnapped the prime minister and most of the government. The December 1991 election became a disaster for the NAR, and PNM was once again able to take over the country with Patrick Manning (1946–2016) as prime minister. After the 1995 elections, PNM lost government power to a coalition of UNC (United National Congress) and NAR, led by Basdeo Panday. The 2001 election, when both parties received roughly the same number of votes, was followed by a period of strong political polarization and unrest, and at the recent election in October 2002, PNM regained government power. The race issue was of great importance for political polarization. UNC was supported by the rural population of Asian origin, PNM by the urban population of African origin.